Syringe Parts and Their Functions
Syringes are essential medical devices used to administer medications, vaccines, and other fluids into the body. Understanding the partes de la jeringa is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals who use these devices regularly. A syringe typically consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in ensuring safe and effective use. In this article, we will delve into the primary parts of a syringe and explore their functions in detail.
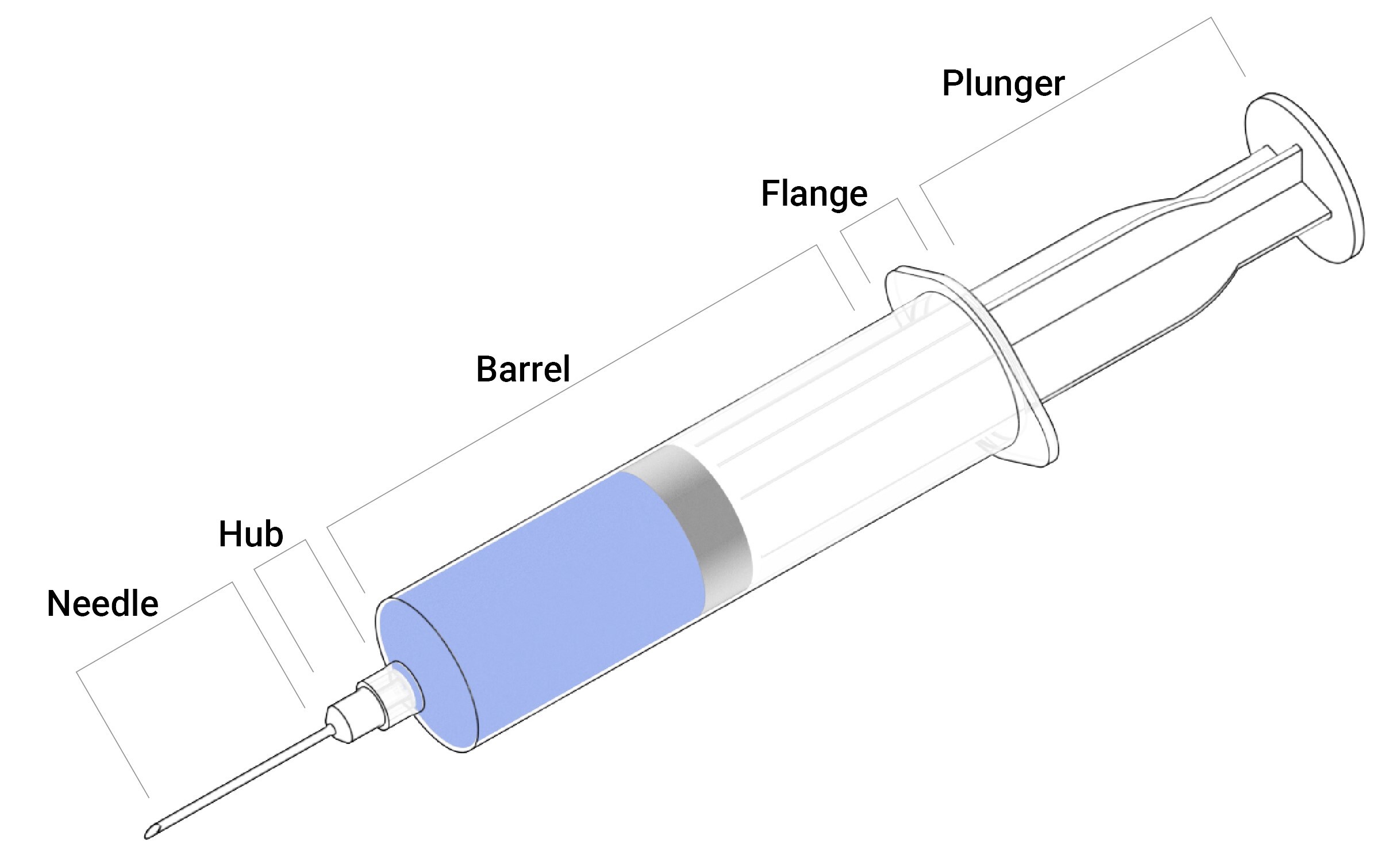
1. Barrel( Cylinder): The barrel, or cylinder, is the main body of the hype. It's generally made of plastic or glass and features graduated markings to measure the volume of the liquid directly. This part is pivotal for icing that the correct cure is administered. The barrel is designed to be transparent, allowing druggies to see the liquid outside, although some hypes may have opaque barrels for light-sensitive medications.
2. Plunger( Piston): The plunger, also known as the piston, is a portable rod that fits inside the barrel. It's responsible for drawing liquid into the hype when pulled back and expelling it when pushed down. The plunger generally includes a rubber gasket or seal at its tip, which helps produce a vacuum and prevents leakage. In some hypes, the plunger may be made entirely of plastic or have a rubber tip attached.
3. Finger Flange and Thumb Rest: These corridor give grip and support when handling the hype.The cutlet flange is located at the top of the barrel, where the stoner places their fritters to hold the hype securely. The thumb rest is deposited at the top of the plunger, allowing the stoner to apply pressure comfortably and control the inflow of liquid.
4. Needle and Needle mecca: The needle is a sharp, concave tube that punctures the skin to deliver drug. It's attached to the hype via the needle mecca, which connects to the barrel. The needle mecca can be secured using a Luer Lock or Luer Slip medium. The Luer Cinch provides a secure threaded connection, while the Luer Slip relies on disunion to hold the needle in place.
5. Luer Lock or Luer Slip: These mechanisms are used to attach the needle to the hype. The Luer Lock is a threaded connection that securely fastens the needle, precluding it from coming loose during use. The Luer Slip, on the other hand, relies on disunion to hold the needle in place, making it easier to attach and detach but less secure than the Luer Lock.
6. Bevel and Needle Cap: The bevel refers to the angled tip of the needle, which helps guide it easily into the skin. The needle cap is a defensive cover placed over the needle when not in use to help accidental pricks and contamination.
Functions of Syringe Parts
Each part of the hype plays a critical part in its overall functionality . Accurate Lozenge The graduated markings on the barrel insure that the correct volume of drug is administered. Fluid Control The plunger allows for precise control over the inflow of liquid, enabling druggies to draw in or expel fluids as demanded. Safety The needle cap and secure attachment mechanisms like the Luer Lock help help accidents and insure safe running. Ease of Use The cutlet flange and thumb rest give a comfortable grip, making it easier to maneuver the hype.
Conclusion
Understanding the corridor of a hype and their functions is essential for effective and safe use in medical settings. By feting the part of each element, healthcare professionals can insure accurate dosing, maintain safety, and give better patient care. Whether for administering specifics, vaccines, or drawing blood, hypes remain a vital tool in healthcare, and their proper use is pivotal for successful medical procedures. See more: https://www.linkedin.com/company/kangyi
